Over time, when using a smartphone, it becomes necessary to obtain Root access to control a device running Android OS. What kind of root rights or access are these, and how to quickly and safely get them on your Android device - you will find out by reading this article.
What are Root rights
Root is the name of a special account for the UNIX operating system or similar systems. The user of such an account can do everything with the software part of his smartphone. As a rule, as soon as you obtain Root access, the warranty on the device is automatically removed. Probably the difference is Chinese smartphones(except Lenovo, Xiaomi and UMI), in which root access is initially open.
Why do you need root access?
Let's take a closer look at what you can do with your smartphone using the capabilities of a super account:
1. Full control of installed “factory” programs. Quite often, the manufacturer installs programs that you will never use, and they take up space.
2. Installation and use alternative programs for creating backups, flashing the kernel, installing patches (software add-ons that add or remove standard system functions), etc.
3. Install the cracked PlayMarket, with which you will have the opportunity to install programs that are not supported by your smartphone.
If all of the above points are necessary, then the only question that remains is how to get Root access to an Android device.
Obtaining Root access using the Kingo Android program
In fact, for every smartphone this procedure is unique and there is always a risk that the device may not turn on after the next firmware update or patch installation. Therefore, we strongly recommend that you think twice before starting.
So, as we wrote above, the procedure is unique for each device, but there are methods that work in 99% of cases. Below we will look at obtaining root access using the software package Kingo Android Root.
The program supports almost all major manufacturers of smartphones and tablets on Android based(Samsung, Nexus, HTC, LG, Lenov, Acer, Sony, etc.). Full list You can look at the website, but as practice shows, it is much larger.
And so let's get started:
1. Download the program from the official website;
2. Then we connect the device to the computer using a USB cable; first you need to enable the “ ” mode. Kingo Andorid will automatically determine what device you have and install the necessary drivers.

3. Once installed required driver just press the "Root" button and wait a bit. If prompts appear, click “Finish”.
4. After root access is obtained, kingo will ask you to reboot the device. Congratulations Root rights have been activated.
Also using Kingo Android Root You can do the opposite; to do this, click the “Remove Root” button. What is truly pleasing is that the program is completely free and safe. But remember, as always, all actions on the device are performed at your own peril and risk.
p.s. Once you have fully obtained super administrator rights, the program can be uninstalled.
How to check if root access has been obtained?
It's not difficult, just go to Play Market In the search, enter root checker and install any of the suggested ones (for example, this one), run it and click the Verify Root Access button. If it says (Sorry! This device has’t root) then access is not granted.
The process of obtaining root rights does not lead to the loss of information or data, so the procedure is painless. The only question after rooting is “Which programs can you trust?” Remember! If the program asks root access- that means she has full control above your smartphone or tablet.
If it doesn't work out for you, you can try.
Root access to the Android system.Root – access is access to the Android system with administrator rights. That is, rooting is a change in the operating system that will lead to the provision of greater capabilities in managing the smartphone.
The very concept of root as a superuser comes from the Linux system, the basis and kernel of Android. Those who have an idea of working in this system know that root is a built-in account system administrator, which has a lot additional features, inaccessible to other ordinary users.
To provide this level of access on your smartphone, simply install a program called su (short for superuser) on it. As a superuser, you can access system files, view cache and do many other things.
Why is this level of access needed?
Does it make sense to do this? The fact is that many applications have been developed that require access from full rights. Their use can significantly expand the capabilities of any smartphone and make working with it much more interesting. These are applications such as Root Explorer, Task Manager For Root, and others. The description of programs of this type indicates that it requires root access.
With full access to the Android system, you can perform many other functions, such as:
Make changes to operating system files, as well as shortcuts and themes;
Delete standard programs operating system;
Run any executable files, designed for Linux;
Create a complete backup copy installed system with all settings and applications, using additional programs;
Launch Tether applications, which will make it possible to use a specific smartphone as an access point (in android versions 2.2 this feature is made standard).
Available firmware with full administrator rights can additionally allow users to install applications on the memory card, transfer the cache to the card, change many system settings, which cannot be accessed through standard menu options, and other possibilities.
You need to keep in mind that simply granting root rights will not add these capabilities to your smartphone; you also need to install the necessary programs, or make changes to the system files yourself.
What types of root access are there?
The Android system has several types of root administrative access:
Temporary root – temporary granting of administrative rights to perform certain functions. After a system reboot, normal user rights return.
Shell root – permanent administrator rights without access to the system folder.
Full root – full permanent unlimited access with administrator rights.
How safe is it?
Of course, such full access to the operating system can be dangerous.
First of all, installing a program on a smartphone that provides root access will void the warranty. This is due to the fact that this level of access can cause irreparable harm to the operating system if handled incorrectly or simply carelessly.
Unfortunately, it is not always possible to return the phone to normal mode. It depends on the specific model smartphone. For some, returning to standard mode does not present any difficulties, for others it is more difficult. Therefore, before enabling rooting, it is worth checking on the Internet about the possibility of returning everything back in the future.
Problems may also arise with installing updates. The fact is that standard updates are installed only on a licensed and unmodified version of the operating system. Therefore, you can return your smartphone to normal mode, install updates, and then switch it back to root mode.
Thus, rooting can provide a lot of additional opportunities to smartphone owners, but at the same time it can become a source of additional danger and headaches.
How to get root access on my smartphone?
On this moment exist as applications for automatic getting root-access for various smartphones literally in one click, as well as applications aimed at hacking a specific model. Among the automated tools, the most famous are:
If you want to dig into the Android system, you may find that many applications require root rights. IN Lately There is practically no need to obtain superuser rights, but some applications still require root rights. This article describes how to root Android and why you might need them.
Why do you need root rights on Android?
Android is based on Linux. On Linux and other Unix-like operating systems, the root user is equivalent to the administrator on Windows. The root user has access to the entire operating system and can do anything. By default, you are not rooted on your Android device, and some apps will not work without root privileges. Like other modern mobile operating systems, Android runs applications in a sandbox for security purposes.
A root user always exists in Android, there's just no built-in way to access it. Getting root rights means that you gain access to account with superuser rights. This process is often compared to jailbreaking an iPhone or iPad, but rooting and jailbreaking are two different actions.
Root rights allow you to do many useful things. With superuser rights, you can uninstall or freeze pre-installed applications, run a firewall, enable tethering even if your carrier blocks it, create a system backup, and use many other settings that require low-level system access.
Applications that require root access are not difficult to find in Google Play Store, but they will not work until you get superuser rights. Some apps have features that work on rooted devices. Therefore, you need to learn how to root Android to take advantage of these features.
Warnings
On Android devices Root rights cannot be obtained for various reasons. In fact, device manufacturers are trying their best to prevent them from obtaining the rights to Android gadget. And that's why:
- Safety: On rooted devices, applications run outside the sandbox. Applications can abuse the superuser rights you have granted and break into other applications, which is usually not possible. That's why Google doesn't approve using Android Pay on rooted devices.
- Guarantee: Some manufacturers claim that after receiving root rights, the warranty disappears. However, gaining root privileges will not break the hardware. In many cases, you can perform the non-root procedure and the manufacturer will not be able to know whether the root rights have been obtained or not.
- Breaking: As always, you do this at your own risk. Obtaining root rights is usually a safe process, but you do it yourself. If you mess something up, you won't be able to count on free warranty service to fix it. If you are worried whether everything will go smoothly, we recommend that you first look for information about successfully obtaining superuser rights on your device to be sure that there will be no pitfalls in the process.
Additionally, rooting may void your warranty, at least for some repairs.
Several ways on how to open root rights on Android
There are many ways to root Android, and which one you should use depends on your phone. In general, rooting will involve one of these processes:
- Unlocking the bootloader: Google and device manufacturers do not officially support rooting, but they do provide an official way for low-level access to some devices, which allows you to later gain root rights. For example, Nexus devices are designed for developers and you can easily unlock the bootloader with a single command. And then get root rights to download the .zip archive containing the file to obtain rights through the recovery screen. The Nexus Root Toolkit for Nexus devices automates this process. Other manufacturers also offer bootloader unlocking methods, but only for certain devices.
- Exploiting a Security Vulnerability: Other devices are blocked. Their manufacturers do not provide an official way to unlock their bootloader and tamper with them software. These devices can only be rooted by exploiting a security vulnerability that allows the necessary file to be installed on the system partition.
- Installing CyanogenMod or other custom firmware on Android: Technically, this is an extension of one of the above methods. Unlocking the operating system's bootloader and exploiting a security vulnerability allows you to install custom ROMs, such as CyanogenMod, which are often already rooted. CyanogenMod has a simple toggle in the settings that allows you to enable or disable root access. Upgrade to new version CyanogenMod or other custom ROM will not disable root rights if the ROM is already rooted.
In this article we will primarily use the first method, which involves an unlocked bootloader. If your phone requires exploitation of a vulnerability, then we will not be able to help you as this process is different for each phone. You can search for information on how to root Android on the XDA Developers forum. You can use the Kingo Root and Towelroot applications, which allow you to gain superuser rights in one click.
Before you can root your android, you will need to unlock the bootloader using the official method and then install the TWRP recovery environment using these instructions. We will use TWRP to root your phone.
How to download SuperSU on your phone and get root access
So, your bootloader is unlocked and you have installed TWRP. Great! You've done almost everything. To root we are going to use the SuperSU program. This best app, which can grant root access to other applications. SuperSU is also available on the Google Play Store, but this version will not give you superuser rights and can only be used if you already have root rights. Luckily SuperSU is also available as a .zip file that we can download from TWRP. This will allow you to gain superuser rights and install the SuperSU application.
So, to get started, follow this link to download latest version SuperSU. Download the .zip file to your computer, connect your phone via USB cable to your PC and download SuperSU to your phone.
Next, boot your phone into TWRP mode. On different phones This is done in different ways, but usually you need to turn off the phone and press and hold the power button + volume up key for 10 seconds, then use the volume keys to go to the “Recovery Mode” item and press the power button to select it.
Once you do this you will be taken to main screen TWRP. Click on the "Install" button.
NOTE: You must make a twrp backup before continuing.
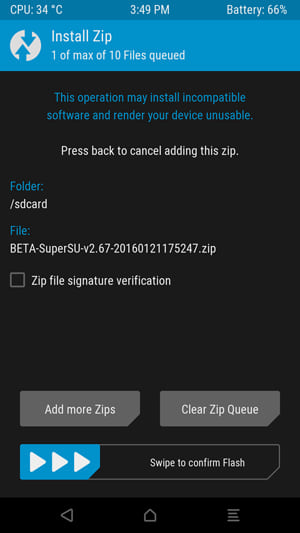
The following screen will appear. Scroll down and navigate to the zip file you downloaded earlier.
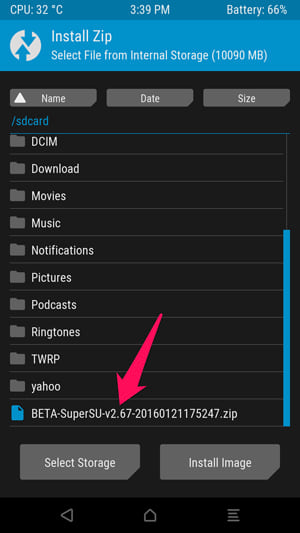
Click on the zip file and you will see this screen. Swipe the slider to confirm installation.
When the process is complete, click on the “Wipe cache/Dalvik” button that appears and swipe the slider to confirm.
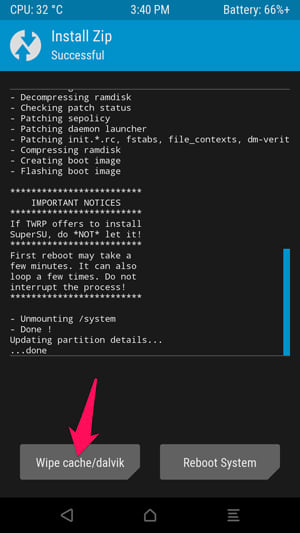
When the process is complete, click on the “Reboot System” button to reboot the Android system.
If TWRP asks whether to install SuperSU, click “Do Not Install”. Sometimes, TWRP cannot detect that you already have SuperSU installed.
Managing root rights with the SuperSU application
Now that you have learned how to open root rights on Android, you need to learn how to manage these rights.
After rebooting your phone, you should see a new SuperSU icon in the application menu. SuperSU distributes rights to applications that require them. Whenever an application wants to ask for superuser rights, it must ask your application SuperSU, which will show this request. To make sure that root rights are working, you can download the Root Checker application to check superuser rights.
For example, let's open and add the Clean Master application, which allows you to clean your device of accumulated garbage. It requires root rights for more effective cleansing. After launch, you will see a message stating that you need to provide superuser rights. Click Submit.
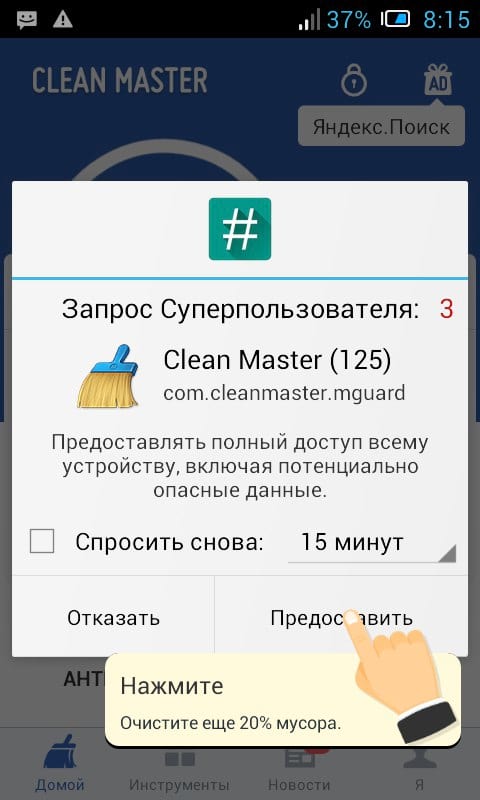
To manage root rights, open the application menu and click on the SuperSU icon. You will see a list of applications that have been granted or denied superuser rights. You can click on an application to change its permissions.
To remove root rights, open the SuperSU application, go to settings and select the option " Complete removal Root". If this is applicable for your device, then root rights will be removed.
Now you know how to open root rights on Android and how to remove them. Good luck!
What is Root? Root (from the English root - root; read “root”), or superuser, is a special account in UNIX-like systems, the owner of which has the right to perform all operations without exception.
What do Root rights give? By gaining access to the main administrator account, you automatically gain not only full control over the operating system with the ability to customize your device according to your preferences, but also possible access for uninvited guests.
Types of Root rights
- Full Root - permanent rights that remove established restrictions. Update operating system Not recommended.
- Shell Root is similar to Full Root, but without access to the system folder.
- Temporary Root temporary Root access. After rebooting the device it disappears.
How to get Root rights?
There are a lot of universal ways and methods for obtaining Root rights on devices running Android control. Most of them involve the use special programs and PC. Several popular programs for obtaining root rights:
- UniversalAndRoot
- z4root
And many more that promise to get what you want in “a couple of clicks.” Unfortunately, not all of them are able to cope with the task relative to yours. mobile device. It is worth noting that such software can be identified as a virus, since it makes changes to the kernel of the Android OS. These programs are indeed viral exploits that penetrate the system kernel and when downloading or installing them, it is recommended to disable security software.
Another way to obtain Root rights is to install modified firmware on your smartphone. In this case, all the work has already been done for you by specialists, and all you have to do is choose the firmware that is suitable specifically for your device. By the way, there you will also find various decorations and additions for your smartphone model.
Please note that some phones have protection supplied by the manufacturer - NAND lock. Most often, HTC was guilty of this, so the owners of such devices were out of luck - NAND lock prohibits making any changes to the /system partition (it will not allow anything to be written/deleted to/from the /system partition, even if it is remounted for writing), which is why It is impossible to install the Superuser program in the /system folder. It is still possible to Root phones with NAND lock, but it will not be fully functional (you can only get Shell root or Temporary Root).
For obtaining administrator or root user rights (superuser) on Android you can use the SuperOneClick program. First, enable USB Debugging mode on your Android smartphone. This can be done through the menu “Settings - Applications - Development”. Connect the communicator to the PC and, if necessary, wait until the driver installation is completed. Launch SuperOneClick. To gain access with superuser rights, click on “Root”. Confirm the installation of BusyBox, wait until the archive integrity check is completed and reboot the device - rooting is complete. For disabling root rights, execute the command “Unroot”.
Obtaining Root access using the program Universal AndRoot 1.6.2, which is installed directly on the smartphone. To get root rights, you can also use applications Unlock Root, z4root, Revolutionary.
How to check that root rights have been obtained?
- It is possible (but not necessary) for an application called Superuser or SuperSU to appear in the list of programs.
- When running programs that require root privileges, a corresponding prompt will pop up
- Programs that previously did not work, citing lack of rights, are now fully functional
- In a terminal emulator, when you enter the su command, a hash prompt appears: #. This verification method depends on the method of obtaining root rights (for example, when using Universal Androot, this verification method is unacceptable). In a terminal emulator, type the command “/system/bin/id”. If you get “uid=0(root) gid=0(root)” in response, then you have achieved what you wanted.
