Any open file, document or program in the Windows operating system will be a desktop area bounded by a frame - a window. It is to this representation that the most popular operating system owes its name, because translated from English “ windows" — window. And that is why it is extremely important to learn how to work with windows. This is the beginning of getting to know your operating system. Let's look at the basic elements of a Windows window and at the same time figure out how to switch between the windows of several running programs.
Basic elements of the Windows window.
We will consider windows using the Notepad program window as an example. Inside the window, there may be some additional interface elements that are specific to each program. However, there are several basic structural elements common to windows of all programs.
When there is not enough visible window space to display the contents of the window, a scroll bar (scroll) appears on the right or bottom. Accordingly, scrolling can be vertical or horizontal. To view, you need to move the mouse pointer over the scroll slider and, pressing the left button, drag in the desired direction. You can also click on the arrows located at the edges of the scroll bar.
In the upper right corner you can see three buttons:
- clicking on the cross will close the window.
- double rectangle means window size reduction.
- if the window has already been reduced in size, there is a square in place of the double rectangle (buttonRestore ).
Clicking on it will return the window to full screen mode. You can also enlarge the window by double-clicking the left mouse button on the top area of the window.

The same result will be if, by dragging the window with the mouse, drag the top border of the window to the top edge of the monitor - the window will expand.
How to switch between windows.
A button that looks like an underscore means Minimize a program to the taskbar . That is, your program still works, but you do not see its working window. If you minimize the program with this button - the "dash", the icon of the minimized program will appear on the Taskbar. If you move the mouse cursor over this icon, you will see a small pop-up window (or even more than one) of the running program.
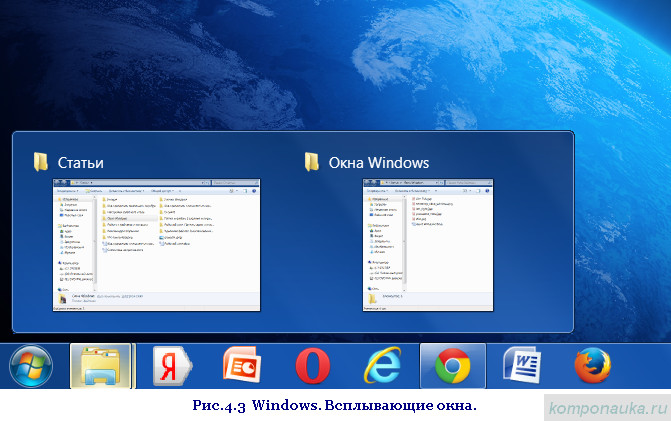
You can click the left mouse button on the icon or on this small window, and the program window will expand to full screen. By closing the "thumbnail" by clicking on the closing cross, you thereby close the program without even calling it on the screen. These miniature windows are very handy if you have several programs open at the same time or several files of one program.
In addition, there is another way to move from one open window to another. Find a key on the keyboard alt and press it. Now find Tab , and, most likely, this key will look like this for you:

Without letting go alt , press Tab . You will see a ribbon of windows running programs. As you press repeatedly Tab , the selection will move across the windows. Stop at the one you want and release both buttons. The selected program will occupy the desktop.
You can minimize all windows by clicking on the oblong button at the bottom right of the Notification Panel. We talked about it when we looked at the Desktop. Keep in mind that when you click on it, the programs will not close, they will only be minimized, and you can “get” them again by finding them on the Taskbar.
If you press the button on the keyboard Win simultaneously with the arrow to the left (or right), the window will occupy exactly half of the working window (left or right, respectively). This is very convenient if you are working in two programs at the same time.


To make a window larger or smaller, you need to move the mouse pointer over the border (frame) of the window or on the corner. The one-sided arrow will turn into a two-sided one. Now, pressing left button mouse, you can expand or shrink the window to the desired size.
To move a window, move the mouse pointer over the bar at the top of the window or over the program title (if there is one) and, pressing the left mouse button, move the window in the desired direction.
There are windows that are directly related to the operation of the system or running program. Their task is to communicate with the user. This dialog boxes. You can't always move them, and you can't change their size either. We will talk about them in more detail.
And that's all for today.
Now we know what isWindows windows and several programs. In the next article, we will talk about what folders and files are and how to create a folder or file.
Waiting for your comments!
We got acquainted with the structure of the window and its device. However, for confident work on a computer, especially for a novice user, this is absolutely not enough.
Let's look at this issue in more detail. We need to learn how to manage Windows windows.
What is meant by this?
Use of window control buttons, various menus and window panels, control of various elements of the window using the mouse and keyboard.
You can do the following basic things with Windows windows:
|
Windows can be in 3 states: normal- looks like a rectangular area that takes up part of the screen, full screen- full screen mode and rolled into a button on the taskbar.
Now everything is in order.
Resizing the window Windows
There are three window controls in the upper right corner. The purpose of each button is easy to find out by moving the mouse cursor over it, holding it down a little, you will see a tooltip with information about the function of the button.
Minimize button - Minimizes the window so that it disappears from the screen and remains as a rectangle on the taskbar. To restore the window on the screen, just click on this rectangle with the left mouse button or right, choosing from context menu the corresponding command (in Windows 7 - from the "Recent" section, select the name of the desired folder or file).

 In addition to the control buttons, you can use system menu window. You can call it by right-clicking on the title bar or on the button of this window in the taskbar (Windows XP).
In addition to the control buttons, you can use system menu window. You can call it by right-clicking on the title bar or on the button of this window in the taskbar (Windows XP).
 Close button - terminates, exits the program, closes the folder window, file (you can also close the window using the context menu of the window button on the taskbar or using the “close” command of the system menu).
Close button - terminates, exits the program, closes the folder window, file (you can also close the window using the context menu of the window button on the taskbar or using the “close” command of the system menu).
The middle button has the dual purpose of Expand and Collapse. 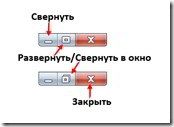 When the window is in normal mode, the button displays a rectangle, clicking on it will expand the window to full screen. The image on the button will change, now it will be a double rectangle. Clicking this button will return the window from full screen to normal window mode. Don't be surprised if a program's window doesn't maximize to Full Screen, the developers simply excluded such a possibility in their program.
When the window is in normal mode, the button displays a rectangle, clicking on it will expand the window to full screen. The image on the button will change, now it will be a double rectangle. Clicking this button will return the window from full screen to normal window mode. Don't be surprised if a program's window doesn't maximize to Full Screen, the developers simply excluded such a possibility in their program.
You can also minimize and maximize the window double click by the title bar, as well as using the context menu of the window button in the taskbar or the “maximize” - “restore” system menu commands.
Restore - returns the size and position of the window to its previous state. The command is active when the window is in full screen mode.
If you have many windows open at the same time, and you need to look at or find something on the desktop, open a folder, a program, instead of closing open windows one at a time and wasting time unproductively on this, you can minimize them all at once. In Windows XP, a special button is provided for this, located in the panel quick start.
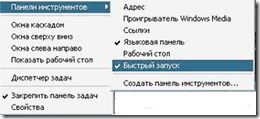
![]() Note that the Quick Launch bar may be disabled. The easiest way to display it is to right-click on the taskbar, select the “Toolbars” command in the context menu, and click on the “Quick Launch” line in the next menu.
Note that the Quick Launch bar may be disabled. The easiest way to display it is to right-click on the taskbar, select the “Toolbars” command in the context menu, and click on the “Quick Launch” line in the next menu.
 In Windows 7, the “Minimize All Windows” button is pinned to the taskbar at the right edge of the screen. All windows can be minimized and maximized using the keyboard shortcut Windows+D
In Windows 7, the “Minimize All Windows” button is pinned to the taskbar at the right edge of the screen. All windows can be minimized and maximized using the keyboard shortcut Windows+D
Moving windows around the screen
To move a window to any place on the screen, align the mouse pointer with the title bar of the window, press the left mouse button while holding it in this position, move the window to another location.
The window can be moved using the window's system menu. By selecting the "Move" command (it is only available in the normal window mode, the cursor becomes a four-way arrow), the arrow keys (these are called "cursor movement keys")  move the window to the desired location and press the Enter key. You can cancel the move mode by pressing the Esc key.
move the window to the desired location and press the Enter key. You can cancel the move mode by pressing the Esc key.
Resizing the window
With — move the cursor (pointer) to the border of the window or to any of its corners and press the left mouse button. The mouse pointer should change to a double-sided arrow. ![]() Without releasing, move the mouse (cursor on the screen) in the desired direction, increasing or decreasing the size of the window. When the desired size is selected, release the mouse. The same operation can be performed using the keyboard. The “Size” command of the window system menu is intended for this purpose; it activates the mode of resizing the window using the horizontal and vertical cursor keys. The command can only be executed when the window is in normal view. When finished moving, press the Enter key. You can cancel an action by pressing the Esc key.
Without releasing, move the mouse (cursor on the screen) in the desired direction, increasing or decreasing the size of the window. When the desired size is selected, release the mouse. The same operation can be performed using the keyboard. The “Size” command of the window system menu is intended for this purpose; it activates the mode of resizing the window using the horizontal and vertical cursor keys. The command can only be executed when the window is in normal view. When finished moving, press the Enter key. You can cancel an action by pressing the Esc key.
But not all windows can be resized, for example, query windows, some dialog boxes.
Organize windows automatically
Open windows can be arranged on the screen in a cascade, from top to bottom (called a "stack" in Windows 7) and from left to right (called a "side" in Windows 7).  "Cascade windows" of the same size, overlap each other so that only the titles are visible, except for the first window.
"Cascade windows" of the same size, overlap each other so that only the titles are visible, except for the first window.
"Windows from top to bottom" and "Windows from left to right" are also the same size, but they are located on the screen next to each other, dividing the screen into equal parts.
"Show Desktop" minimizes all open windows to the taskbar and allows you to see the desktop without open windows.
"Cancel ..." (last command).
To arrange windows in one of the above ways, select one of the listed commands from the context menu of the Taskbar. 
Switching between windows
It is positioned as a multitasking system, in which you can simultaneously work with several windows, programs, documents, moving from one to another. Any open windows the operating system considers a running task. Switching between windows is actually a transition to another task.
If there are several open windows (running tasks), only one of them can be active, the one in which you are working, all others are inactive at that moment.
What is the visual difference between the active window:
its title is brighter, in other windows the titles are dull, less saturated color;
button on the taskbar active window differs in color or looks more prominent than the buttons of other windows;
the active window is in the foreground, obscures other windows (unless it is above or nearby).
The main ways to switch between windows:
Numerous windows open folders, programs, and documents clutter up your desktop, making it hard to keep track of them. Therefore, it is important to learn how to quickly switch between the necessary windows. Ways to move from one window to another:
When many windows of the same program are open, the buttons are grouped (this function must be configured in the taskbar properties). 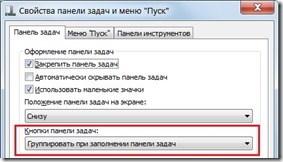 To select the desired window, click on the group button and select it from the list.
To select the desired window, click on the group button and select it from the list. 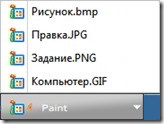
If you have a gray outline when you move a window, and then the window itself moves, do the following:

We have seen the possibilities of resizing a window, moving windows, minimizing all windows, and switching between windows in the Windows operating system.
Perhaps this information on the blog will be useful to you, your friends or relatives, share it, press the buttons social networks. Share your experience in the comments, ask questions if you have problems and difficulties.
When you have dozens of windows open, switching between them can be inconvenient. However, you can always make the work a little more comfortable.
Key switching
In Windows operating systems, there is a special keyboard shortcut that allows you to quickly switch between windows. This combination is Alt + Tab. However, it works a little unusual in comparison with other hot cases. Pressing this combination once will move you between the last two active windows, and holding the Alt key and pressing and releasing the tab key will select any of the open windows in sequence. To go to the window, simply release the Alt key.
If there are too many windows open and you accidentally skipped the right one by pressing Tab while holding Alt, then just add to the combination Shift key- in this case, the selection of the active window among the open ones will be carried out in the opposite direction.
Another way to switch between windows from the keyboard is the combination Win+Tab. In some Windows versions these keys opened a 3D window selection interface, and in Windows 10 they open the so-called "Task View" (which may also have a button on the Taskbar). This view shows all open windows, which can be simply selected with the mouse.

Also, through the "Task View" you can add additional virtual desktops and transfer open windows between these tables. In some cases, this greatly facilitates the work - some of the cases are located on one desktop, some of the cases are on the other. The number of virtual desktops can be up to a hundred.
Convenient window arrangement
Often, when working, it would be nice to have several windows in front of your eyes at once. In this case, the question arises of their convenient location relative to each other. And the option of overlapping one window with another is definitely not suitable here. Windows allows you to quickly arrange windows on equal parts of the screen, splitting the workspace into two or four parts.

Simply grab the application window by its title bar with the cursor and drag either to the edge of the screen or to one of the corners. By bringing the cursor to the edge of the monitor, the window will automatically take up either half of the space (when brought to the edge) or a quarter (when brought to the corner). For convenience, it is immediately suggested to select the next active window, which will automatically take the dimensions for the location next to it. You can switch between such windows simply by moving the mouse cursor, and often there is simply no need for switching itself - it is enough that the information we need is already in front of our eyes.
Switch between office documents
If you are actively working with office documents V Microsoft applications Office, you might like the developer's solution for quickly switching between windows. Working with text editor Word, electronic Excel spreadsheets And PowerPoint presentations, pay attention to the "View" tab, where the button with the name "Go to another window" is located. Clicking on it will open a list open files in the application of the same name. Just click on the name of the one you need to make it active.
Since Windows is a multitasking system, you can open several windows at once in it, switching from one window to another if necessary. Among all open windows, one is active is the window that is currently being worked on, and the others are inactive or passive .
Signs of an active window:
The title of the active window is brighter than the titles of other windows.
The button of the active window in the Taskbar appears to be pressed, while the buttons of other windows appear to be depressed.
The active window is positioned on top of other windows.
For operating system all open windows are considered tasks, regardless of whether an application window or a folder is open. To switch to another task means to make the corresponding window active.
Ways to switch between windows:
click on the window button in the taskbar;
click on any visible area of the inactive window;
use the Alt + Tab key combination - press the Alt key and, without releasing it, press the Tab key. This will bring up a panel with icons for all open windows. When the desired icon is highlighted, release both keys.
Alt+Esc - toggles between non-minimized windows.
b) Creating folders and files in windows environment In order to create new file or a folder in any other folder on your computer's disk, you need to do the following sequence of actions: navigate to the folder in which you want to create a new folder or file. It can also be the root partition of your drive; right-click on any point free of icons in the folder you open in the main working window of Explorer; in the menu that appears, select the New item and in it specify the type of file object you want to create. By default, Windows offers to create the following types of file objects: Folder - new folder; Shortcut - new shortcut; Briefcase - portfolio; Picture (Bitmap Image) - graphic file; Text document (Text Document) - a text document in Pain Text format; Sound WAV (Wave Sound) - sound file; Compressed ZIP folder - a folder compressed using the WinZIP archiver built into Windows XP. If additional applications and software packages are installed on your system, for example Microsoft office or any graphic editors, this menu may also contain other items, such as a vector drawing, a Word document, or a Microsoft Excel sheet. After the new object is created, you will need to enter its name from the keyboard. The name can be specified in both Latin and Cyrillic characters.
V) File name extension(eng. filename extension, often just say a file extension or extension) - a sequence of characters added to the file name and designed to identify the type (format) of the file. This is one of the common ways that a user or computer software can determine the type of data stored in a file. The extension is usually separated from the main part of the filename by a dot. In CP/M and MS-DOS operating systems, the length of the extension was limited to three characters, in modern operating systems this restriction is not. Sometimes multiple extensions can be used in succession, such as ".tar.gz". In the FAT16 file system, the filename and extension were separate entities, and the dot separating them was not really part of the full filename and served only to visually separate the filename from the extension. In the FAT32 and NTFS file systems, the dot has become a common legal character in a filename, so restrictions on the number of dots in a filename on those systems and their locations have been lifted (with some exceptions, such as all trailing dots in filenames are simply discarded). Therefore, the standard search pattern *.* no longer has any practical meaning, it is enough to specify *, since the dot character now falls under the concept of any character.
22. a) Clipboard(English clipboard) - an intermediate data storage provided by the software and designed to be transferred or copied between applications or parts of one application. An application can use its own clipboard, available only within it, or a shared one provided by the operating system or other environment through a specific interface. The clipboard of some environments allows you to paste copied data in different formats depending on the receiving application, interface element, and other circumstances. For example, text copied from a word processor can be pasted with markup into applications that support it, and as plain text into others. You can paste an object from the clipboard as many times as you like. As a rule, when information is copied to the buffer, its previous contents are lost. But, for example, Microsoft Office contains several buffers, so it can store several pieces of information at the same time. Some desktop environments include a program to log the latest buffer values and retrieve those that have already been overwritten. !!!Hot keys for using the clipboard
A list of some so-called hotkeys that will make working with your computer a little more convenient and faster. The list, of course, is incomplete, but includes the main keys and keyboard shortcuts that a novice user needs to know. In addition, it is very useful to get used to controlling the computer using the keyboard (in case if the mouse fails, For example).
Del(or Delete) is used to delete files.
Win(window button Windows on the bottom row of keys on your keyboard) - brings up the Start menu.
Ctrl+Esc also brings up the start menu.
Left Alt + Shift- this keyboard shortcut is usually in Windows switches the input language.
F1- challenge Windows Help.
F10– activates the menu bar of the open program.
Enter is the equivalent of clicking on the highlighted button.
Esc- the equivalent of a button click Cancel.
Pause- if you press this button on the keyboard while the computer is booting, you can view information about it: the frequency of its processor, the size hard drive, capacity random access memory etc. After viewing this information, to further boot the computer, press the key Esc.
Prt Scr(Print Screen) - By pressing this key, you can take a snapshot of the screen of your computer monitor. Then just open some graphical editor, for example, Paint, and paste the image from the clipboard there (to paste, use the keyboard shortcut ctrl+v, or simply click Edit > Paste from the program menu. Then save the drawing to JPEG format or JIF. For Windows Vista: If instead Prt Scr press the key combination Alt + Print Screen , then Windows Vista will not copy the entire screen to the clipboard, but only the current window that is displayed on the screen.
Shift– If this key is kept pressed, inserting a CD cancels the autorun procedure (AutoRun or CD player).
PageUp- Scrolls up the page of an open document or browser.
PageDown- scrolls down the page of an open document or browser. Keyboard Shortcuts:
Ctrl+Esc- opens the menu START.
Alt+Tab- switching between open programs.
Alt+Tab+Shift- switching between open programs in the opposite direction.
Alt+F4- closes the current window.
Shift+Del- deleting an object without moving it to BASKET.
Ctrl+O- calls the "Open document" window in any program.
ctrl+w- closes the document in any program.
Ctrl+A- By clicking, you can select the entire document in any program.
ctrl+s- saves the document in any program.
ctrl+c- click to copy the selected part of the document or file to Clipboard.
ctrl+v- click to insert part of a document or file from Clipboard.
Win+Pause/Break- open control panel window system-properties.
Win+R- opening the "Start Program" window (the same as START → EXECUTE).
Win+D- Minimizes all currently open windows.
Win+F- opens a window SEARCH.
Win+Tab- toggles between buttons on Task Panels.
Standard shortcuts for working with clipboard used in graphical user interfaces on PC-compatible PCs (for PC101 keyboard with QWERTY layout): Copy selected objects to clipboard: Ctrl + C or Ctrl + Ins . Cut selected objects to clipboard (to move): Ctrl + X or ⇧ Shift + Del . Paste from clipboard: Ctrl + V or ⇧ Shift + Ins . Although these combinations are the most common, some applications may use other key combinations. For example, in the X Window System, in addition to the above-described clipboard, a "selection" buffer is available, to copy into which you just need to select the desired part of the text, and to paste, just press the middle mouse button or simultaneously the left and right buttons (imitation of the middle button).
b). Context menu(English context menu) in the graphical user interface - a menu that opens, as a rule, when you press the second button of the pointing input device. This menu displays commands provided by the object (context) that was under the pointer at the time it was called, and general commands. Whether an object has a context menu and what it contains depends on the operating environment and the specific program.
e). Main menu Windows systems ( Start menu - menu Microsoft Windows, launched by clicking the Start button on the taskbar or by pressing the Windows logo key on your keyboard. It is the central starting point for launching programs as well as opening recent documents and accessing system properties. First appeared in Windows 95. Starting with Windows XP, there are two options: "Classic" - similar to the one in Windows Me/2000/98/95, and "Standard" - the default in Windows XP, Windows Vista, in which you can run frequently used programs. In Windows 7, there is only a standard variant of the design of the Start menu, but there is no classic one. Windows XP Start Menu: Displaying the user's name and avatar Accessing the browser and E-mail client Accessing frequently used programs Opening special folders Turning off the computer
23.
TEXT EDITOR
WORD General view Text editor Word is designed to compile any documents: business and personal. Word is launched either through Start -Programs - Microsoft Word, or by double-clicking the program's shortcut (if there is one on the desktop). Opens automatically on startup new document named Document1 (DOC1.DOC). This name remains until you change it when saving to disk. Title Bar Program Menu Bar Title Bar Toolbar Document Toolbar Standard Formatting Ruler Scroll Bar Status Bar Figure 1 Microsoft Word Window working area there is a vertical cursor. Recall that the TEXT CURSOR is a vertical stroke that indicates where text will be entered next. You can move the text cursor INSIDE THE TEXT using the mouse (to do this, click the mouse button in the place where you want to place the cursor) or using the cursor keys and the following keyboard shortcuts:
MICROSOFT WORD is a word processing application. It can be used to create letters, reports, invoices, brochures, novels, and other text documents. A text document is any information displayed on a computer keyboard. Documents created in WORD can contain both text and graphics, and other objects such as sound and video clips. WORD makes it easy to format characters and paragraphs. Built-in spelling and grammar checking programs check the document not only after it is completed, but also during creation. Existing object manipulation tools allow you to create attractive documents for printing, displaying on the screen and posting on the INTERNET. Finally, the HTML format support provides a good tool for beginner web page designers. Download WOPD. Standard: Start Microsoft programs WORD Through the Microsoft OFFICE panel Through the program shortcut. Through the opening WORD document. Screen view. Window WORD programs contains standard window controls: Title; Menu bar; Toolbars - Standard and Formatting; Scroll bars; Status bar. The menu bar of the WORD program consists of the following sections: File - work with document files. Edit - editing the document. View - setting the program window and document type. Insert - Insert pictures, diagrams, mathematical formulas, non-standard symbols and other objects into the document. Format - document formatting (setting font, paragraph, style, etc.). Service - service functions (spell check, WORD settings). Table - work with tables. Window - work with document windows. ? - reference information about WORD. Usually on the screen we see two toolbars Standard and Formatting. They contain buttons for quick access to menu commands. If you move the mouse pointer over any button, a tooltip appears, and a brief description of that command appears in the status bar. Let's consider some commands of the first three menu items, studying the corresponding buttons in parallel. File menu. Create. When this menu item is selected, a dialog box opens in which we can select a template for the created document: General, Letters and faxes, Notes, Other documents, WEB pages. The New button on the toolbar quickly creates a regular document. Open. Selecting this menu item opens a dialog box where we can find desired document to read, edit, or print. This menu item corresponds to the Open button on the toolbar. Close. This command closes an open document. It corresponds to the y button in the upper right corner of the document window. Save. This command is for saving an open file to this moment document. When this command is selected for the first time or when the save button is clicked, a dialog box appears in which we can specify the name of the file in which the document will be saved and, if necessary, the folder. Selecting this command again will save the document in the same file. Save As... If you need to make a copy of the document or save it elsewhere (for example, on a floppy disk), then use this command. In the dialog box, you need to specify a different name or path. Page settings. This command sets the page parameters for placing the document on it. The dialog box consists of 4 tabs: Margins, Paper Size, Paper Source, and Layout. Let's consider the first two. On the Margins tab, indents are set from the edges of the paper to the beginning of the text. The distance is indicated in cm. On the Paper Size tab, we can select a standard size or specify it in cm (if the printer allows it) and the orientation of the text on the sheet - Portrait or Landscape. Preview. This command shows how the document will look when printed. To her
Hotkeys in Word: 1. Text selection by words - Shift+Ctrl+cursor. Selects text not by characters, but by words, which speeds up the selection of the phrase as a whole. 2. Selecting a line to the end - Shift + End. Selects text from the position where the cursor is to the end of the line. 3. Selecting a line to the beginning - Shift + Home. Selects text from the position where the cursor is to the beginning of the line. 4. Select all text to the end - Shift + Ctrl + End. Selects text from the position where the cursor is to the end of the entire text. 5. Select all text to the beginning - Shift + Ctrl + Home. Selects text from the position where the cursor is to the end of the entire text. 6. Make the selected text bold - Ctrl+B. 7. Select text in italics - Ctrl + I. 8. Underline text - Ctrl + U. 9. Cut - Ctrl + Del. 10. Copy - Ctrl + C. 11. Paste - Ctrl + V. 12. Transfer to the next line without a paragraph - Shift + Enter. 13. Transfer to the next line from a new page - Ctrl + Enter. 14. Change the case of the selected text (lowercase, uppercase, first capital) - Shift+F3.
