What is root rights on Android? Their types
Those who have worked with the Linux system before have probably come across the concept of root rights before. The term "root" means a "superuser" account, that is, the main administrator. If we have access to this record, our possibilities are greatly expanded. They are not available to the general user.
For example, if we root Android, we will be able to open Linux system executable documents, take screenshots using programs like ShootMe, perform backups, use the mobile device as a hotspot, change shortcuts and themes, as well as make changes to system files and remove pre-installed applications. We add that the use of a mobile device as an access point is relevant for platform versions up to 2.2, since later this function received the status of a standard one.
Having root rights, we will also be able to open various special programs (like Titanium Backup or SuperUser), transfer the browser cache to the card, etc. However, you should be aware that it is better for an ordinary, “non-advanced” user to abandon the idea of obtaining root access. Firstly, he does not need it at all, and secondly, he risks causing irreparable damage to his apparatus.
Allocate full unlimited root rights on an ongoing basis (full root), permanent rights without access to system folder(shell root) and temporary root rights (temporary root).
So, we figured out what root rights are on android. Note that not every owner of a mobile device can get such access. Some of the devices have a NAND lock, and without overcoming it, you cannot change the system folder and get full root. However, the user will be able to rely on shell root as well as temporary root.
How to get root rights for Android?
At the moment, you can access it using one of the many methods described on the web. In this case, you should also take into account the model and brand of your mobile device.
One of the universal ways can be called obtaining root rights using the Framaroot program. This is a very simple method. It is also valid on many devices. A good option is to use Kingo Apps android root, as well as VRoot.
Please note that the utilities that usually give you the rights of the main administrator are recognized by our devices as containing viruses. It is recommended to disable anti-virus software first.
According to statistics, more than 60% of owners mobile phones operated by the operating room Android systems they do not know what Root rights are and what they give the user. And absolutely in vain! After all, only having full access to the phone, you can do anything with it - change hidden system settings, install and remove any programs. And even among those who were able to get privileged access on their smartphone to install some application, not everyone can clearly answer what Root is on the phone and why it is needed.
root is a superuser in Linux-based operating systems (including Android). It has a unique identifier 0, as well as the rights to absolute access to all parameters and perform any tasks. For ease of understanding, I will give the following analogy - Root rights on Android are almost a complete analogue of the Administrator in Windows.
Root Pros:
+ Full access to OS system settings + Ability to delete system files + Access to phone hardware settings + Ability to delete pref installed programs+ Installation of custom firmware on the deviceCons of Root-rights:
In some cases, a complicated procedure for obtaining rights - Possible loss of warranty (if interference is proven) - You can damage the phone and even turn it into a "brick" - Emergence of vulnerabilities in the system due to full access - Not all devices can get Root "but.
Why Root Rights are Needed on Android
Now let's take a closer look at what rights are given to Ruth and why they are needed.
For inexpensive devices with little internal memory, the most relevant reason for obtaining privileged access is the ability to remove all unused pre-installed applications.
The second most popular reason for getting Root rights on Android smartphones is the ability to edit system files and, in particular, the bootloader for subsequent installation of custom firmware on the device.
The third reason is the need to install a specialized software, which requires privileged access.
What are the types of root rights
full root- This is permanent full access to system files and settings. Permanent administrative rights without any restrictions. This option usually excludes the possibility of automatic firmware updates.
Temporary Root- Temporary full access to your phone or tablet. Almost an analogue of full Root-rights, with the only exception that after rebooting the device they will disappear.
Shell Root- in this case, you will get root rights with limited access to the system folder /system/. In this case, you will not be able to edit and make changes to the files in this folder, as well as use a number of functions.
fastboot- this is not exactly getting Root-rights. These are special programs designed to test the device. By connecting the device to a computer, you can use the fastboot to launch any files and install custom firmware on your phone.
Systemless Root- this is the so-called "non-system root". Another option for rooting a smartphone on Android. In this case, all modified files are installed in the "/su" folder, while nothing changes in the "/system" system directory. Instead, all modified files are installed in the "/su" folder. Non-system Root-rights allow you to update your phone with official firmware without any problems.
Android has taken over the world. This operating system from the American Internet giant Google is installed on most mobile devices various price categories. It is it that is distributed according to the most attractive scheme, so any manufacturing companies can install it.
To access hidden settings, you will need to get Superuser rights
Android is complete operating system, so it can be used to perform a variety of tasks. We will not now consider in detail the capabilities of the system. If you have questions, we advise you to read. In order to take full advantage of all the possibilities and hidden settings, you need to root your Android. In this article, we will look at what root rights are, as well as all the available options for obtaining them.
What are root rights for?
First, let's talk about how the system works. When the user starts work, the system activates his account, which stores the main settings and preferences, as well as installed programs. Thanks to this, there is no need to reconfigure the device every time it is turned on. If you sync your tablet or smartphone with an account Google entry, settings and the list of applications will be stored on the remote server of the company.

For most users, the options for setting up the device that are provided by the developer are quite enough. For full control over the file system and settings, as well as for the ability to fully configure the device, an account with root rights is required. On Linux, of which Android is an offshoot, this is called "superuser mode", on Windows it's called Administrator mode. If in computer operating systems it is enough to enter with a password account(Windows) or enter it if necessary system settings(Linux), then in the mobile you need to carry out certain procedural steps to obtain root rights.
What exactly is their presence?
- Absolute control over the device system.
- The ability to change system applications, remove or replace them.
- transformation desired applications to system.
- Advanced features for creating a full-fledged backup.
- Changing the boot menu to install new firmware or modify an existing one.
- Opportunity fine tuning appearance Android.
- Transfer system applications to a memory card in case of its small volume in the device.
- Complete removal of unnecessary applications.
- Remove ads not only in the browser, but in all applications.
- Processor and hardware improvements.
The list is far from complete, you can list many more advantages that the superuser rights provide. But is it that easy to get them?
Options for obtaining root rights
The fact is that Google, together with top manufacturers, in every possible way hinders the process of obtaining root rights. Firstly, the user has the opportunity to disable ads, and Google makes very good money on this. Secondly, the company believes that most users have crooked hands, and if they have a root, they will definitely ruin something.
![]()
There are several ways to get root rights. In some cases, you can get by with just one mobile application, in others you will need a computer and a special rooting program. You can also get superuser rights by logging into recovery mode. There is no universal way that is effective for each device.
Types of root rights
Depending on the type of device, you can get one of the varieties of root:
- full, or full root - working constantly and without any restrictions, providing full access to the system partition; you can change everything at your discretion;
- partial, or shell root - also works on , but has a number of limitations, the most significant of which is the lack of access to system partition files; many opportunities become unavailable;
- temporary, or temporary root - gives full or partial access to all file system, but only until the first reboot of the device; after turning it on again, root flies, and you have to repeat the whole procedure again.
Android Application
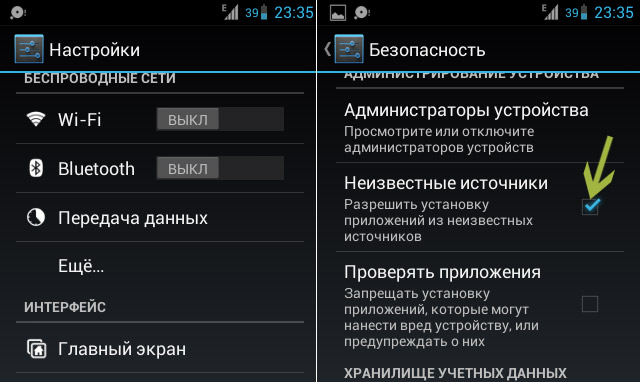
Most easy way obtaining root rights. You just need to allow the installation of programs from unknown sources (to do this, activate the corresponding item in the Settings - Security menu), download the application installation file, install it and run it. After that, you should perform all the actions that the program requires. The whole process usually only takes a few minutes.
The most famous:

There is also other software. If you are unable to achieve results with the above programs, try to find others.
computer program
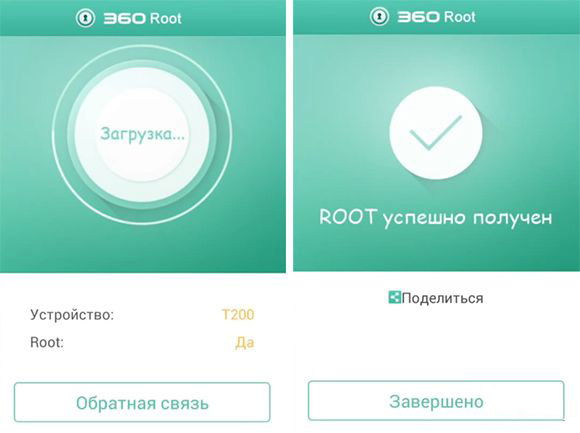
It also allows you to quickly root with a few clicks on your computer. Algorithm for obtaining rights through a computer:

There are several programs, the most popular of them - Kingo Root, OneClickRoot, VRoot. If you are unable to cope with your device using one program, you can try another.
Using recovery mode
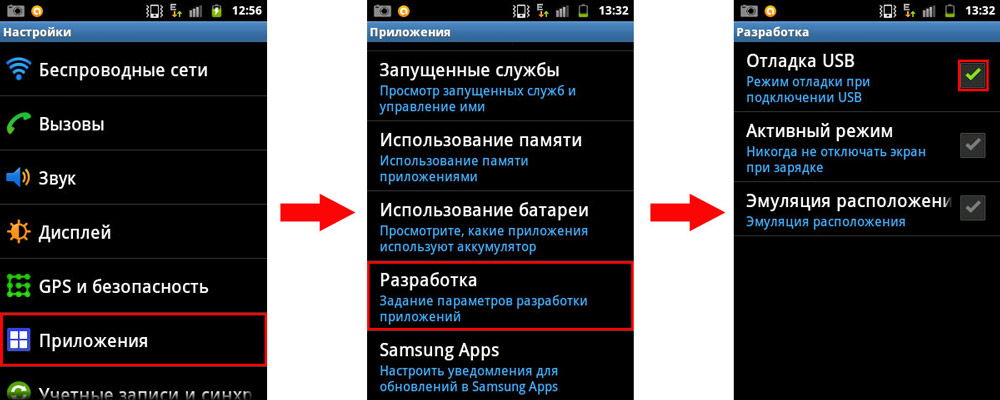
The method is simple, but it requires certain skills and care, because if you do not comply with one of the conditions or accidentally skip a step, you can only complicate your life. Recovery mode is a recovery mode that allows, in case of incorrect operation, to reset, clean system cache or install an update. It starts most often by simultaneously pressing the power and volume buttons when the device is turned on. The combination may vary. To get root in this way, you will need:
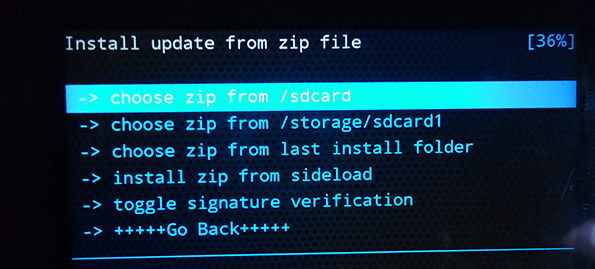
- download a zip archive with modified files, called update.zip, and copy it to the root of the memory card;
- enter recovery mode, go to install zip from sdcard - choose zip from sdcard and select your archive;
- after the process is finished, click reboot system now to reboot the device.
No matter how confident you are in your abilities, we recommend that you clarify the information specifically for your model on specialized forums. So you protect yourself from possible unpleasant consequences.
Possible risks
Despite the many advantages, there are several fat disadvantages:
- Your warranty is automatically void. In the event of a breakdown, you will have to carry out repairs entirely at your own expense.
- It becomes impossible to automatically update the firmware through the device menu.
- There is a risk of rendering the device inoperable.

IN Lately manufacturers are releasing more and more advanced ones that are practically unhackable.
Conclusion
As you can see, getting root rights for android procedure simple, but in some cases there may be insurmountable difficulties. We strongly advise you to study the pages of your device on specialized forums, for example, w3bsit3-dns.com or xda-developers.com. There you will find comprehensive information about all possible difficulties, comments from specialists or experienced users, and more precisely decide which method is best for you - through a computer or on the device itself. Are you planning to root your device? Do you think they are needed? We are interested in your opinion on this matter.
Denis Zaichenko,
July 2, 2014, 00:04
Man wants freedom. Another thing is that it is not always clear to him why it is needed at all - some individuals can live calmly in a cage, being aware of this, others will not have enough space on the whole continent. It depends on the person himself, on his upbringing, childhood, friends and enemies. Everyone is unique and everyone goes their own way. For a smartphone user, access to root rights is not a vital function. This is, let's say, a fallback. Is there iPhone users, which have never done Jailbreak, and are not going to. And here it is not a matter of skill, but of need. If your pocket friend on Android performs the functions for which he was bought, the question of the need for shamanism is removed. But in the event of a feature hunger that an advanced user visits, root rights become a tasty morsel. And today we will discuss the main pros and cons of this action.
First, a little materiel. Just a little, don't worry. The word root in the Linux environment is an account that has certain privileges in accessing files. It is also called the superuser. The closest exact comparison is the administrator profile in Windows, only a password is usually not needed. However, it depends on the device, and now we are not talking about a full-fledged Linux, but about its offspring mobile format named Android.
So, imagine that your computer is accessed through an administrator profile. You can edit system files, cheat with the registry, crap in the cache and do other operations that, with a certain level of curvature of the hands, can lead to the transformation of the PC into a photo frame with a permanent BSOD on the screen. So, the superuser in Android has an even harder time, because you can make more mistakes, but simply reinstalling the OS on it is not an easy task. To summarize: superuser rights allow the smartphone owner to access system files, and, more importantly, modify them and save these changes.

It will not be superfluous to say that there are three types of root rights. Full Root provides the user with permanent access to the superuser's capabilities, Shell Root is a trimmed version of Full, that is, changing the / system folder is not available, and Temporary Root gives full access only until the smartphone is rebooted. And now:
Flaws
The warranty period for most types of electronics ranges from six months to two years. During this time, it is possible to identify after-sales defects, the responsibility for which lies with the manufacturer. If he really is to blame (which is easy to check), repairs and replacement of components will be made free of charge at special service centers. But if the so-called warranty conditions are violated, you will have to do everything at your own expense. So, getting a superuser account violates the terms of the guarantee in 99% of cases. It's like opening the security seals on the TV to try to fix it yourself, but not succeeding in this, send the device to the SC. The warranty conditions are violated, the manufacturer does not know for what reason the breakdown occurred - through his fault, or through yours. And no one will take it on faith.

Therefore, I form the first and main drawback for the average user: when you get root access, you will almost certainly lose the warranty on your smartphone! True, there is an option that with a certain chance can hide such actions - a rollback to the factory firmware, but only those who have already dealt with access to the system at a low level are able to do this. Although the probability of an error for such users is close to zero, the root “counter”, if the manufacturer has inserted it, may not be reset. Well, if the warranty for the device has already ended, then there is no point in fearing this particular drawback.

In mine, I mentioned that with the opening of superuser rights, the smartphone receives an additional pack of vulnerabilities. But this applies not only to the fact that even a simple virus can easily shit in the holy of holies - right in the heart of a pocket friend. People are naturally curious. Having gained unheard of freedom in working with a smartphone, they try to do things while diligently avoiding the study of materiel. Their self-confidence amuses, but the result is not very good. With a careless hand movement, a multifunctional phone turns into a so-called. "brick", which does not even turn on. This means that a man-made grain of sand got into the impeccably debugged mechanism and stopped the work of the gears. For the average user, the matter is solved exclusively service center, flashing and losing all data (!) that were in the phone, except for those on the memory card and SIM card. And the SC, in turn, will require money from you for this service, because the guarantee has expired (see the paragraph above).

This implies the second drawback: if you make an error in working with superuser rights, you can disrupt the operation of the OS up to irretrievable data loss. You can avoid this by the following actions: before doing something, you need to find out the consequences - there is probably at least one person on the Internet who has already taken a risk and posted his thoughts in an accessible form. Next - always have a backup copy on hand, and more than one. I'm not talking about gallery files or contacts, but about a full-fledged backup of the entire system - the so-called recovery. How to do it, we will discuss later.

Also, for a user who has tasted the delights of root for the first time, the following news will be sad: interference with system files will take away the smartphone’s ability to automatic update, that is, to receive new firmware versions. Yes, yes, you won’t see KitKat if you are on older versions of Android and decide to play around with the superuser. However, there is no question of reliability here - an update may come, and even be installed, and even work! But if this happens to you, consider yourself winning three lotteries in a row, because this is a colossus with feet of clay, and your OS runs on files that are not designed for this. Therefore, disadvantage number three: after obtaining root access, you can forget about auto-updates of the smartphone OS, unless you are a very lucky person. If you really want a new one android version, you have to do everything manually. It's not easy, but since you got root access, if you please, respond to this title!

A serious drawback of root rights is the variability of obtaining them from device to device. Let's start with the fact that not every smartphone generally provides such an opportunity. If your device has a feature (although I would call it a "crutch") called NAND lock, you can not dream of rooting. About Full Root, to be precise. The other two options are available in most cases. Yes, there are ways to get around this software charm, but be prepared for additional hours of digging through instructions.

There is no complete list of devices with NAND lock, but even if your smartphone does not prevent getting root access, do not expect it to be easy. There is no single recipe for obtaining superuser rights. Each novelty will be studied by Internet masters for the first few days, before a sequence of actions appears on the Western forums. Do not even think that it will be simple - there can be more than 20 steps, and each of them includes a desktop computer, the Internet, third party programs, stubs and the devil knows what. Conclusion: due to NAND lock, not all smartphones have the ability to get Full Root, and for most devices where this option is available, there is a separate instruction that you need to look for a long time and strictly follow it. And if something didn’t work out on the way to your goal, there is a high probability of getting a technological “brick” at a reasonable price.

And the last but very important fact. Any experiments with getting root-rights, changing the firmware, creating a backup on a PC or creating a recovery should be carried out ONLY through the NATIVE USB cable, which should be plugged DIRECTLY into the computer case, bypassing any hubs. The fact is that various Chinese crafts of any price and cost, with the exception of branded peripherals, fail at the most important moment, or simply cannot cope with such tasks. This is not a phenomenon of recent days - not even siemens phones flashed only through native USB, which, by the way, cost a lot of money and was quite rare. As a result, it is possible to make a smartphone an expensive brick in the process of obtaining, say, recovery, which should protect the user from such situations. Be careful!
Advantages
The freedom of action. By obtaining Root rights, you, as a smartphone user, will acquire full control above the device. Do not like standard applications? Get rid of them! Tired of standard labels/icons? For God's sake, change them to whatever you like! You can remove the splash screen when you start and turn off the device, you can make the native flash dance during a call, you can put artificial limits on Internet traffic, remove ads from applications, hide the notification bar or navigation menu, and much, much more. Of course, for such changes, appropriate programs are needed.

Don't feel like messing around with individual elements, but the standard look of the shell is frankly bored? There is a solution! With root rights, no one will stop you put the real custom firmware. The CyanogenMod project can be considered the leader in this field, within which software builds for dozens of popular devices are released daily ... But there is also MIUI, Illusion, ParanoidAndroid and many others. After getting to know them, you may want to go back to such a native and understandable factory firmware, but not everything is not so simple, and the specifics specific device won't be slow to tell. Down with doubt! The possibilities of individual ROMs are simply breathtaking.

For example, the main advantages of CyanogenMod are the initial purity (no unnecessary preinstalled programs), ease of use, a minimum of settings with the ability to quickly switch profiles, as well as excellent optimization. Among the shortcomings, it is worth highlighting a small set of settings, as for custom firmware, as well as general instability in work. A MIUI firmware positioned as a hybrid of Android, iOS, and, in fact, is a hodgepodge of the best elements of both platforms. It doesn't have a majority. preinstalled apps, but there is a large number of themes and widgets, and most of the standard for android applications either removed or replaced with "lighter" counterparts.

Illusion stands out for its completely transparent interface, auto-hide status bar and excellent notifications, which can be configured separately. ParanoidAndroid is generally a kind of sandbox with customization, which is respected by individual Linux distributions. This includes scaling EVERY single program, the status bar can also be customized as desired, as well as notifications, and the overall interface layout can be changed from smartphone to tablet, and PIE Control combines all the main shortcuts into one convenient diagram.

But there is even more customizable firmware - AOKP. Personally, it reminds me of the times when Siemens phones ruled the roost, as you could do incredible things with them. With AOKP, your vibrator will start singing along with your favorite song, there will be a photo of your girlfriend instead of uploading, and the Ribbon interface will negate the need for launchers. And that's just short review what universal ROMs are capable of. But there are still firmware for individual devices that fix the most unpleasant errors without rearranging the design on its head. Often they are almost in no way inferior to stock. But also nice little things, like the built-in boot menu, the ability to record screencasts or change the screen density in dpi through a general scaling. ATTENTION! The latter function is extremely dangerous, and can lead to "bricking the smartphone."

If you are a specific user and need the same functionality, for example, to run executable Linux files, then, in principle, Root will help you. However, I can assure you - there are compilers that work without superuser rights. And the process itself rests on the difference in library compatibility that these same compilers and cross-compilers overcome. The very capabilities of a smartphone, which has everything necessary to run it, will allow you to at least keep a web server, and, at a maximum, run Wine. And then walk the soul.

Another reason for obtaining superuser rights, which has become decisive for me, is the ability to use programs to create screenshots. It would seem that any Android smartphone user can do this right out of the box thanks to special key combinations. But this situation can be compared with the PrintScreen button and with some Fraps in Windows. It's one thing to hold down several buttons to get one picture, and quite another - without looking up from the game process, press a single touch button that is projected over applications. In such programs, the quality of the image is easily adjusted, you can set the location of the button, set the serial shooting. In general, if you need to frequently take screenshots from your smartphone, Root will be extremely useful.

Remember the articles about backing up smartphone content (Part 1, Part 2)? There is another type Reserve copy, which is called recovery. As an example, let's take Windows again - if all previous backup options were backups contents of the Gallery, as well as games and programs, then the recovery is OS files, without which the computer will not work. Therefore, if your smartphone has turned into a brick and does not start, a regular backup will not save it, but it will save the recovery. And exactly the latter requires superuser rights to create, and special program , like Orange Backup.

As you can see, it's not that simple Root rights mi. But no matter how experienced you are, no matter how much recovery burdens your computer and no matter how many custom firmware you have seen in your life, remember:
"With great power comes great responsibility!" Uncle Ben
